Codebase Indexing
Codebase Indexing transforms how Roo Code understands your project by creating a semantic search index using AI embeddings. Instead of searching for exact text matches, it understands the meaning of your queries, helping Roo find relevant code even when you don't know specific function names or file locations.
What It Does
When enabled, the indexing system:
- Parses your code using Tree-sitter to identify semantic blocks (functions, classes, methods)
- Creates embeddings of each code block using AI models
- Stores vectors in a Qdrant database for fast similarity search
- Provides the
codebase_searchtool to Roo for intelligent code discovery
This enables natural language queries like "user authentication logic" or "database connection handling" to find relevant code across your entire project.
Quick Start Guide
You can set up codebase indexing at zero cost by using:
- Qdrant Cloud (free tier) or Docker Qdrant (completely free)
- Google Gemini (currently free)
This gives you professional-grade semantic search without any subscription fees!
Step 1: Choose Your Setup
Before enabling codebase indexing, you'll need two components:
- An Embedding Provider - to convert code into searchable vectors
- A Vector Database - to store and search those vectors
Step 2: Set Up Qdrant (Vector Database)
Option A: Cloud Setup (Recommended for Getting Started) - FREE
- Sign up at Qdrant Cloud (free tier available)
- Create a cluster
- Copy your URL and API key
Option B: Local Setup - FREE
Using Docker:
docker run -d \
--name qdrant \
--restart unless-stopped \
-p 6333:6333 \
-v qdrant_data:/qdrant/storage \
qdrant/qdrant
Using Docker Compose:
services:
qdrant:
image: qdrant/qdrant
ports:
- "6333:6333"
volumes:
- qdrant_storage:/qdrant/storage
volumes:
qdrant_storage:
Step 3: Set Up an Embedding Provider
Google Gemini Setup (Recommended) - FREE
- Get an API key from Google AI Studio (currently free)
- In Roo Code settings:
- Provider: Google Gemini
- API Key: Your Google AI Studio key
While this guide focuses on Google Gemini since it's currently free, Roo Code also supports OpenAI, Ollama, OpenAI-compatible, Mistral, Vercel AI Gateway, Bedrock, and OpenRouter providers. You can explore these options in the configuration dropdown.
Step 4: Save
- Click Save and Start Indexing
The status indicator will show:
- Yellow (Indexing): Currently processing files
- Green (Indexed): Ready for searches
- Red (Error): Check troubleshooting section
Managing and Configuring the Indexer
You can monitor the status and manage all configuration for the codebase indexer directly from the Roo Code chat interface.
The Status Icon
At the bottom-right corner of the chat input, you'll find the Codebase Indexing status icon. This icon provides a quick, at-a-glance overview of the indexer's current state.
The color of the icon indicates the state:
- 🟢 Green: Indexed. The index is up-to-date and ready for search.
- 🟡 Yellow: Indexing. The system is actively processing files. Searches can still be performed, but results may be incomplete.
- 🔴 Red: Error. An issue has occurred (e.g., failed to connect to Qdrant or the embedding provider). See the Troubleshooting section for help.
- ⚪ Gray: Standby. The indexer is waiting for configuration or has been disabled.
Multi-Folder Workspaces: In multi-folder workspaces, each folder maintains its own indexing status and configuration. The status icon reflects the combined state of all workspace folders.
The Configuration Popover
Clicking the status icon opens the main configuration popover. Here, you can view the detailed status and manage all settings.
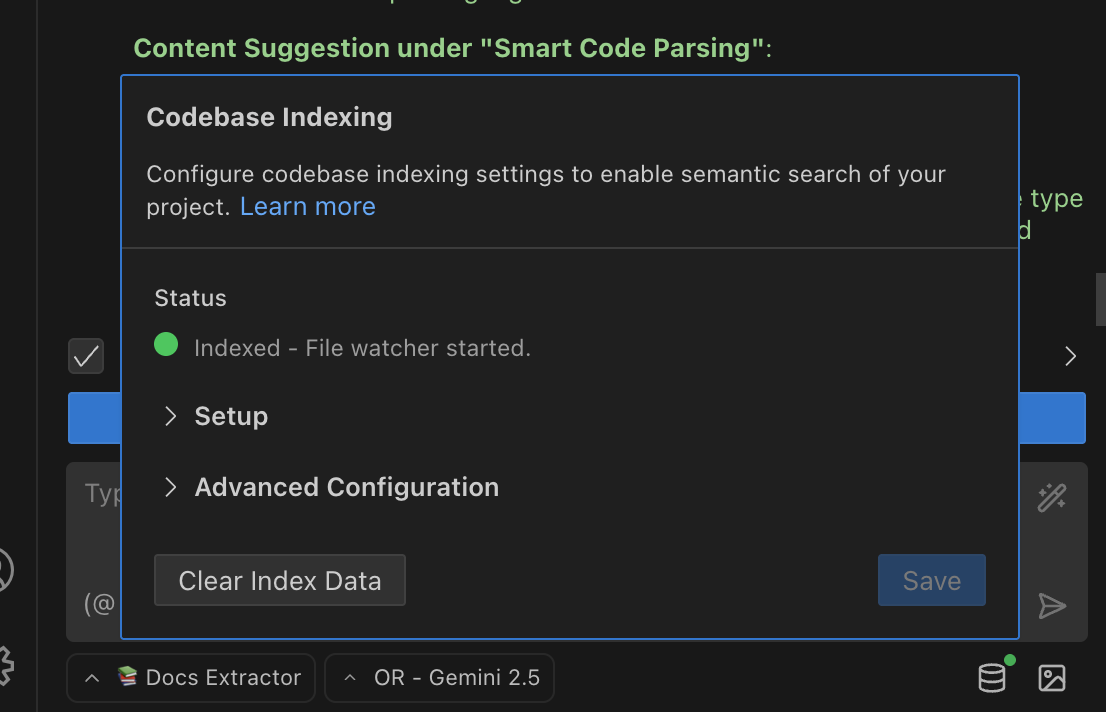
- Status: A detailed message showing the current state, such as "Indexed - File watcher started" or the progress of an ongoing scan.
- Setup: Contains the primary fields for connecting to your embedding provider and vector database.
- Advanced Configuration: Allows you to fine-tune search parameters like the similarity threshold.
- Clear Index Data: Deletes all data from the Qdrant collection and clears the local file cache. Use this when you want to re-index your entire project from scratch. This action cannot be undone.
- Save: Applies your configuration changes. If a critical setting (like an API key or a model) is changed, the indexer will automatically restart.
Detailed Configuration Fields
This guide explains each setting available in the configuration popover.
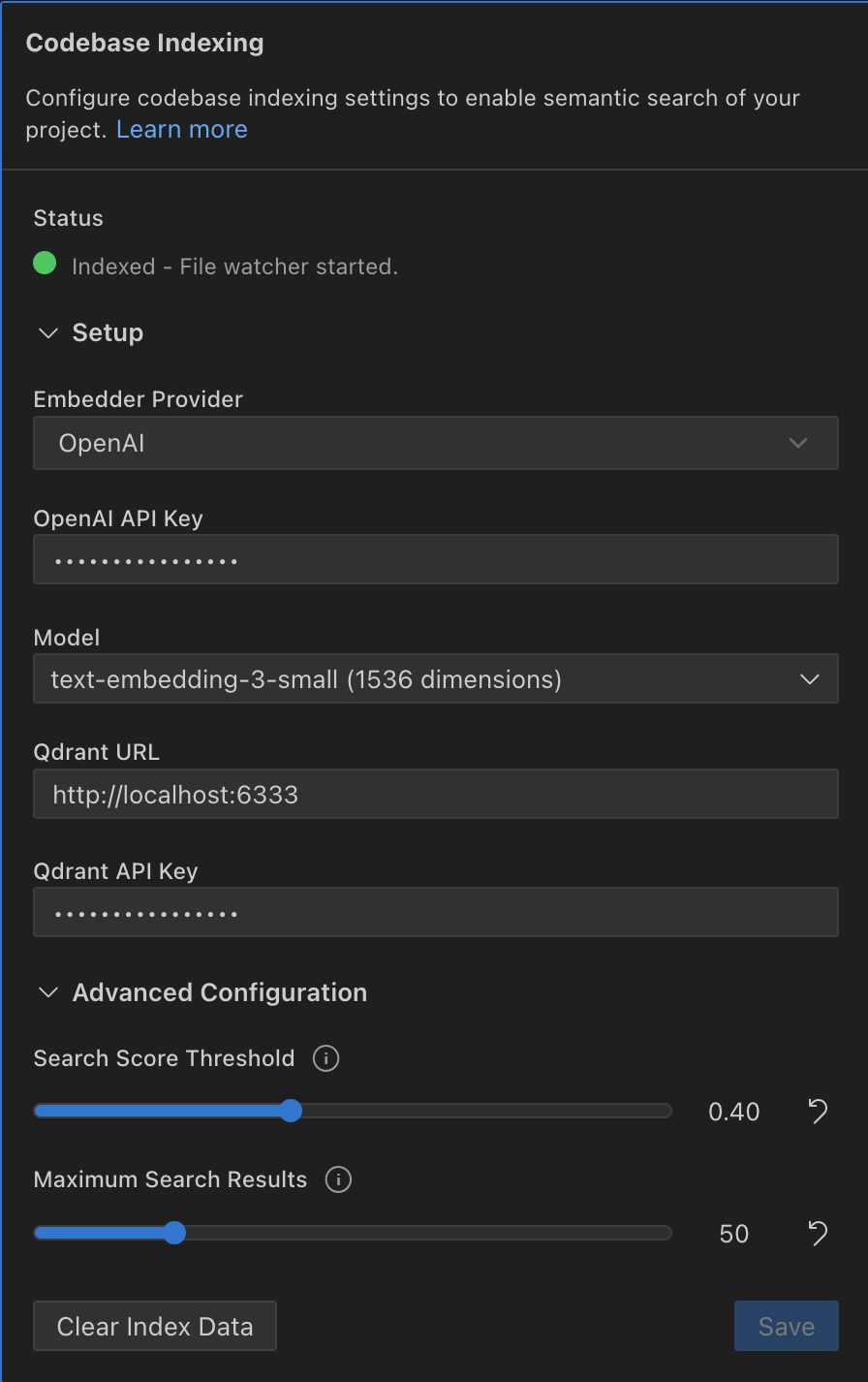
Setup Fields
-
Embedder Provider
- Purpose: To select your source for generating AI embeddings.
- Behavior: This dropdown menu determines which configuration fields are shown. Your options are OpenAI, Google Gemini, Ollama, OpenAI Compatible, Mistral, Vercel AI Gateway, Bedrock, and OpenRouter.
-
API Key (for OpenAI, Gemini, OpenAI Compatible)
- Purpose: The secret key to authenticate with your chosen provider.
- Behavior: This input is required for all cloud-based providers and is stored securely in your VS Code secret storage.
-
Base URL (for Ollama, OpenAI Compatible)
- Purpose: The endpoint for connecting to the provider's API.
- Behavior: For Ollama, this is typically
http://localhost:11434. For OpenAI Compatible providers like Azure, this is the full deployment URL.
-
Model
- Purpose: To select the specific embedding model you want to use.
- Behavior: The list of available models changes based on the selected provider. The model's vector dimension (e.g.,
1536 dimensions) is displayed, as changing dimensions requires a full re-index.
-
Qdrant URL
- Purpose: The connection endpoint for your Qdrant vector database.
- Behavior: This must be a valid URL pointing to your local or cloud-based Qdrant instance (e.g.,
http://localhost:6333).
-
Qdrant API Key
- Purpose: The authentication key for a secured Qdrant instance.
- Behavior: This field is optional and should only be used if your Qdrant deployment requires an API key.
Advanced Configuration Fields
-
Search Score Threshold
- Purpose: Controls the minimum similarity score required for a code snippet to be considered a match.
- Behavior: Use the slider to set a value between 0.0 and 1.0. A lower value returns more (but potentially less relevant) results, while a higher value returns fewer, more precise results.
- Recommended Settings:
- Low (0.15-0.3): Broader results, good for exploration
- Medium (0.4-0.5): Balanced precision and recall (default: 0.4)
- High (0.6-0.8): Precise matches only
-
Maximum Search Results
- Purpose: Sets the maximum number of code snippets returned by a single
codebase_search. - Behavior: Use the slider to adjust the limit. This helps control the amount of context provided to the AI.
- Purpose: Sets the maximum number of code snippets returned by a single
Key Benefits
- Semantic Search: Find code by meaning, not just keywords
- Enhanced AI Understanding: Roo can better comprehend and work with your codebase
- Cross-Project Discovery: Search across all files, not just what's open
- Pattern Recognition: Locate similar implementations and code patterns
How Files Are Processed
Smart Code Parsing
The system uses a sophisticated parsing strategy:
- Tree-sitter First: For supported languages, it uses AST parsing to identify semantic code blocks (functions, classes, methods)
- Markdown Support: Indexes Markdown files by treating headers as semantic entry points
- Intelligent Fallback: For unsupported file types, it falls back to line-based chunking
Block Sizing:
- Minimum: 100 characters
- Maximum: 1,000 characters
- Large functions are split intelligently at logical boundaries
File Filtering
The indexer respects your project's ignore patterns:
- Files matching
.gitignorepatterns - Files matching
.rooignorepatterns - Binary files and images
- Files larger than 1MB
Important: Ensure your .gitignore includes common dependency folders like node_modules, vendor, target, etc., as the system relies exclusively on these patterns for filtering.
Incremental Updates
- File Watching: Monitors your workspace for changes in real-time
- Smart Updates: Only reprocesses modified files
- Branch Aware: Automatically handles Git branch switches
- Hash-based Caching: Avoids reprocessing unchanged content
- Multi-Folder Workspaces: Each folder in a multi-folder workspace maintains its own index with separate settings and status
Best Practices
Writing Effective Queries
Instead of searching for exact syntax:
- ❌
const getUser - ✅
function to fetch user from database
Use natural language descriptions:
- "authentication middleware"
- "error handling for API requests"
- "database connection setup"
Security Considerations
- API Keys: Stored securely in VS Code's encrypted storage
- Code Privacy: Only small code snippets sent for embedding
- Local Processing: All parsing happens locally
- Access Control: Respects file permissions and ignore patterns
Troubleshooting
Connection Issues
"Connection to Qdrant failed"
- Ensure Qdrant is running (
docker psto check) - Verify URL matches (default:
http://localhost:6333) - Check firewall/network policies
- For cloud instances, confirm URL and API key
"Invalid API Key" or "401 Unauthorized"
- Double-check your API key is correct
- Ensure the key has necessary permissions
- For Ollama, verify the service is running
API Key Format Errors (“ByteString conversion”)
- Symptom: Error mentions "ByteString conversion" during indexing or when saving settings
- Likely cause: Your embedding provider API key contains invalid/special characters or hidden whitespace
- Fix:
- Regenerate a fresh API key from your provider dashboard
- Paste the key again, ensuring no leading/trailing spaces or hidden characters
- Roo will display a clear validation message if the key is invalid
Model Issues
"Model Not Found"
- For Google Gemini: Ensure the model name is correct (e.g.,
gemini-embedding-001) - For other providers: Consult their documentation for available models and proper naming
Indexing Issues
"Stuck in Error State"
- Check connection issues first
- Click "Clear Index & Re-index" in settings
- This resolves corrupted cache or collection issues
"Indexing Taking Too Long"
- Normal for large codebases (10k+ files)
- Check
.gitignoreincludes large directories - Consider adding patterns to
.rooignore
Using the Search Feature
Once indexed, Roo can use the codebase_search tool:
Example Natural Language Queries:
- "How is user authentication handled?"
- "Database connection setup"
- "Error handling patterns"
- "API endpoint definitions"
- "Component state management"
The tool provides:
- Relevant code snippets
- File paths with line numbers
- Similarity scores
- Direct navigation links
Privacy & Data Security
Your code stays private:
- Only small code chunks (100-1000 chars) sent for embedding
- Embeddings are one-way mathematical representations
- Local parsing means full files never leave your machine
- Use Ollama for completely offline operation
Data Storage:
- Vectors stored in your chosen Qdrant instance
- You control where data lives (local/cloud)
- Easy to delete: just clear the index
Current Limitations
- File Size: 1MB maximum per file
- External Dependencies: Requires embedding provider + Qdrant
- Language Support: Best results with Tree-sitter supported languages
Future Enhancements
Planned improvements:
- Additional embedding providers
- Multi-workspace indexing
- Enhanced filtering options
- Team collaboration features
- VS Code native search integration
- Incremental re-indexing optimizations